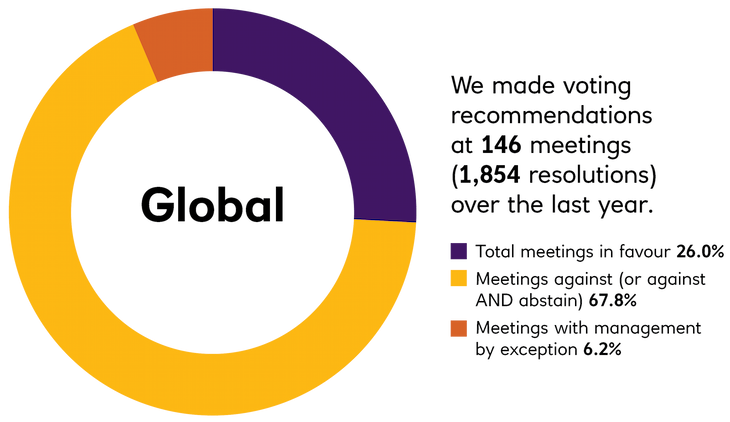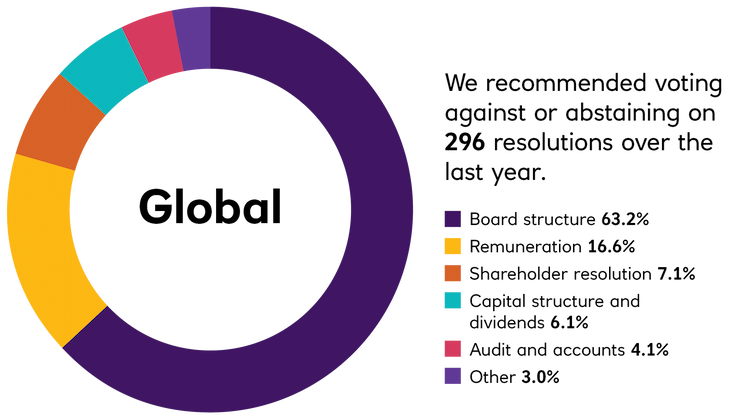Engage and vote
The Trustee has exercised its ownership rights and engaged with investee companies in investment grade credit through its stewardship manager, EOS. Engagement work carried out with EOS is in collaboration with other EOS clients and is based on mutually agreed priorities in the EOS engagement plan. This is more efficient and effective than attempting to engage as an individual investor. Engagement in private investments takes place through the relevant investment managers or board representation.
The EOS Annual Voting and Engagement Reports for the Fund are made available on the Trustee website and a summary of this activity is set out in the Fund’s implementation statement which forms part of the annual report and accounts. The key points to note from voting and engagement activity in 2023 are set out below (with 2022 and 2021 activity shown for comparison).
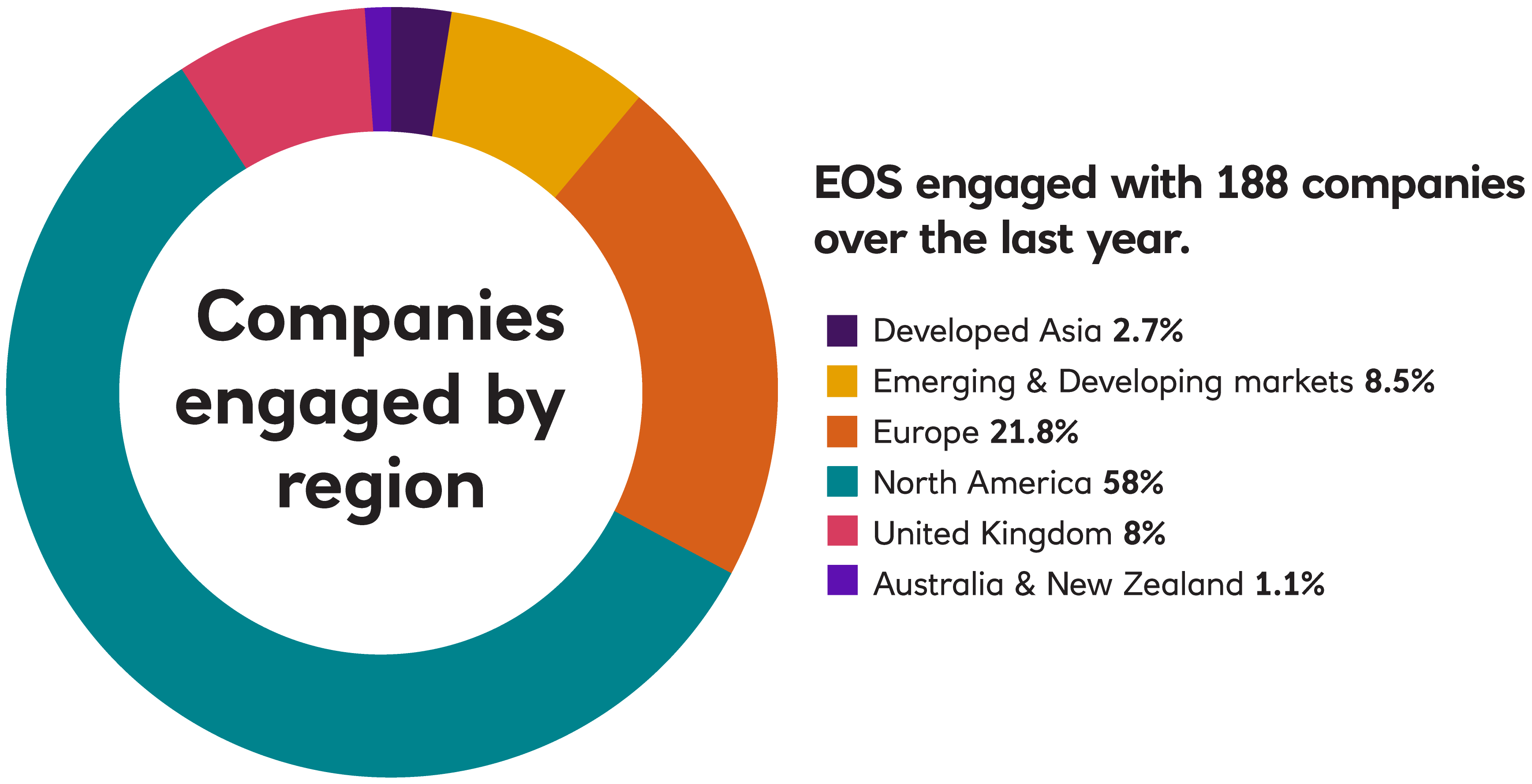
EOS Engagement by Region
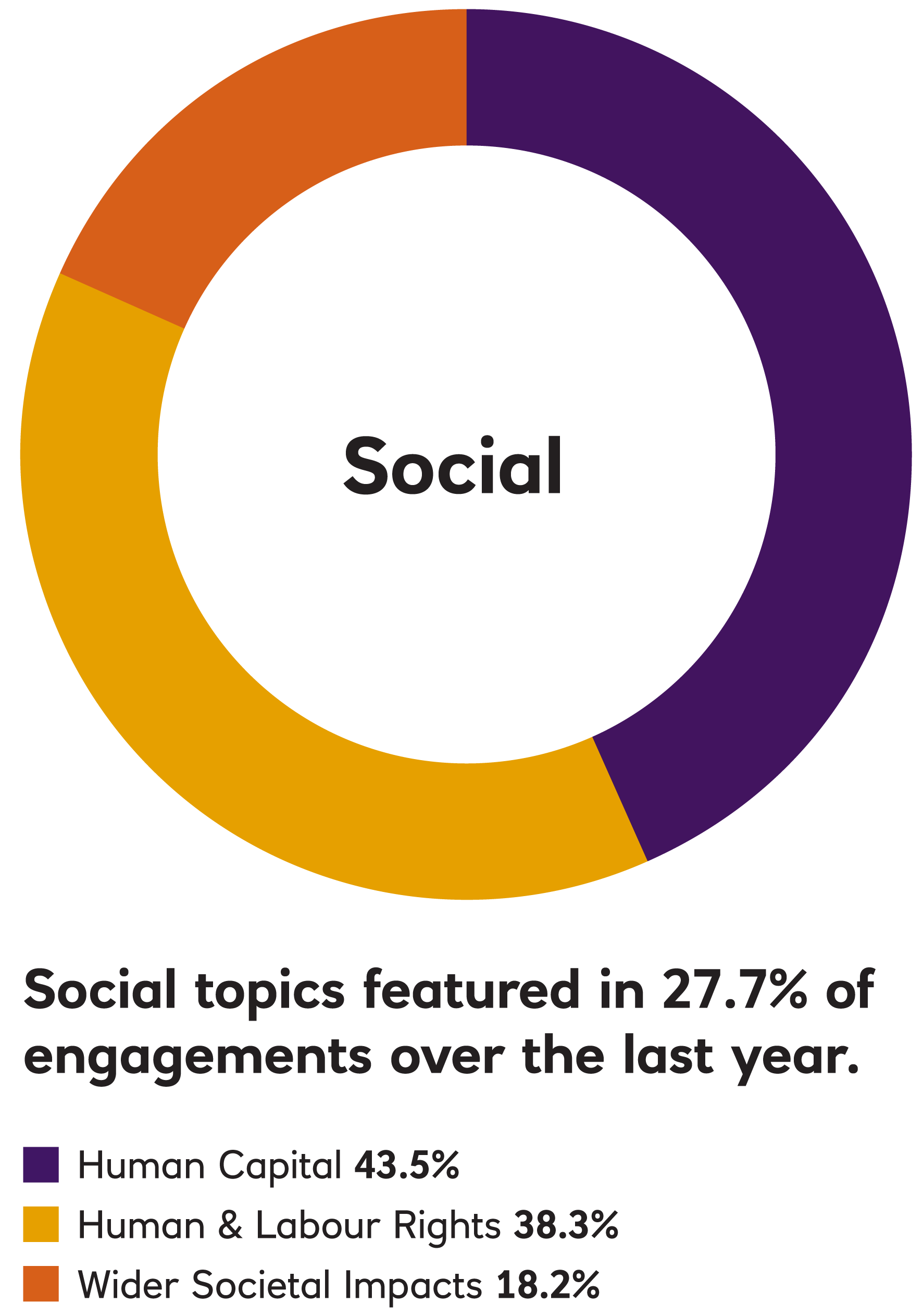
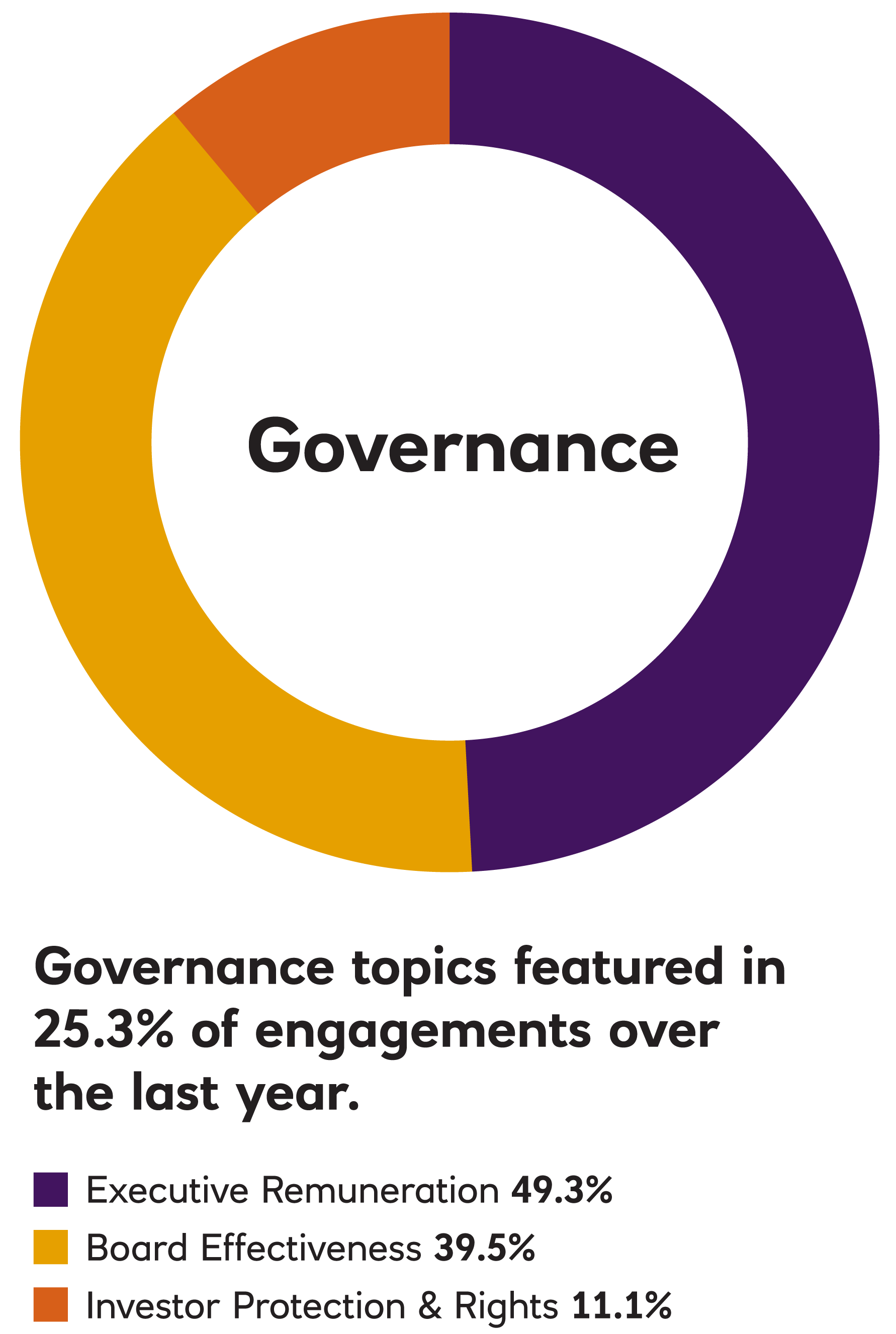
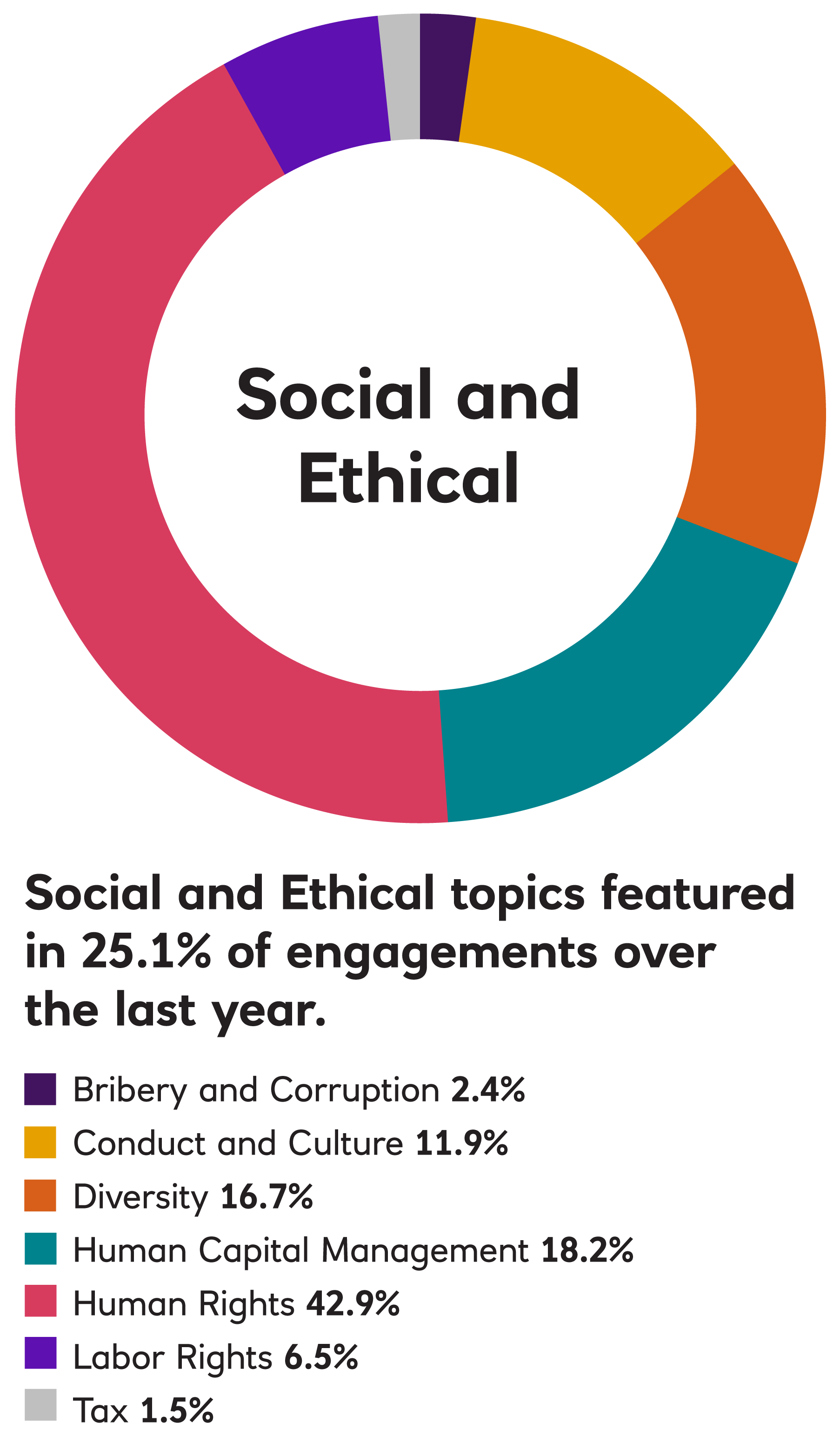
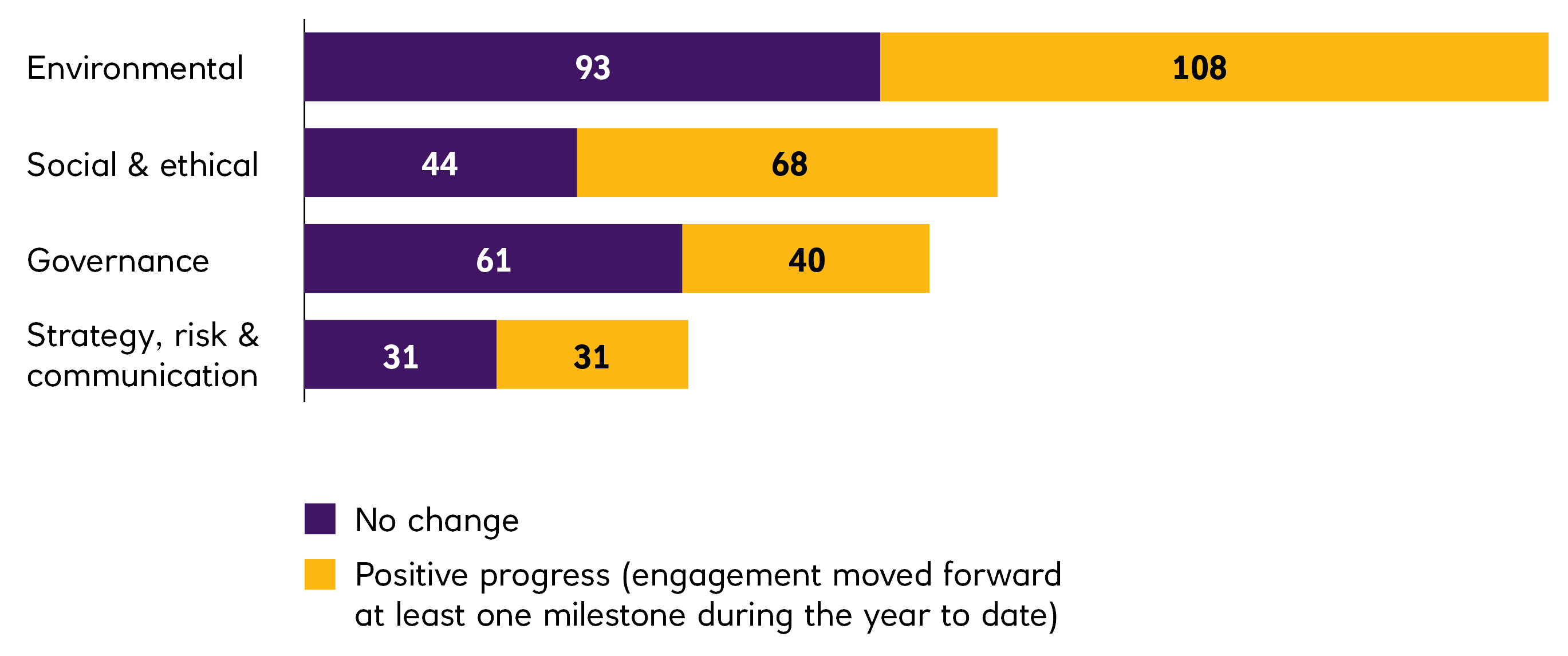
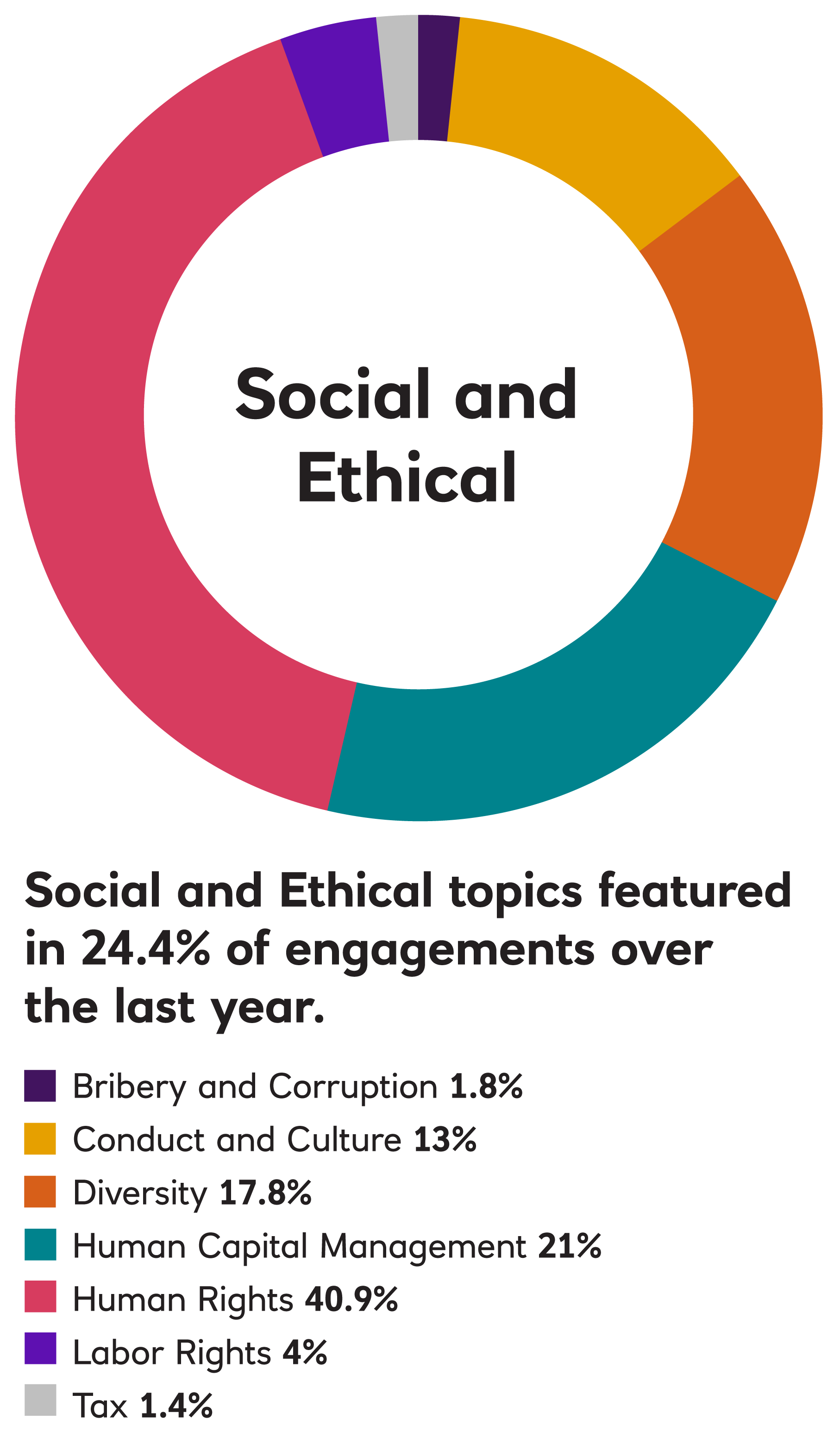
In 2023, EOS engaged with 188 companies on 1,169 environmental, social, governance, strategy, risk and communication issues and objectives.
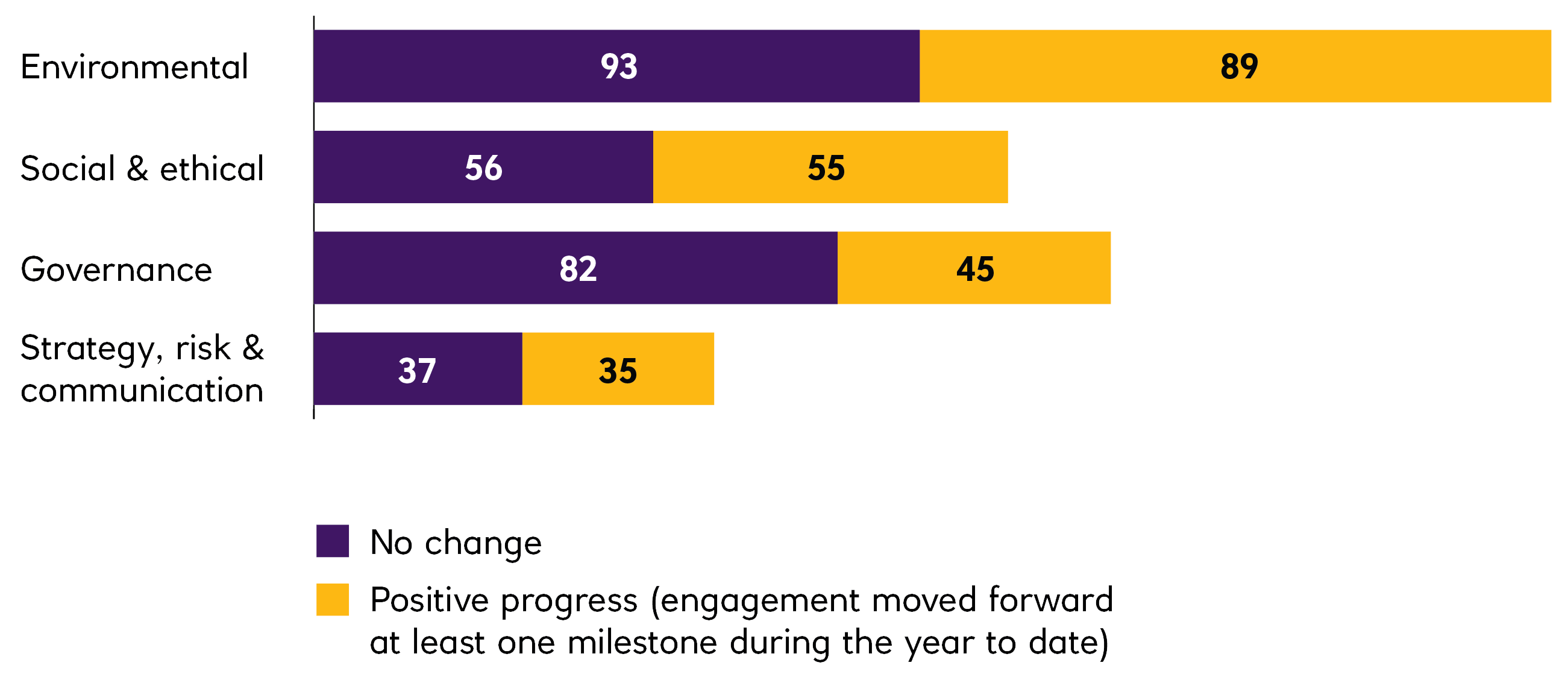
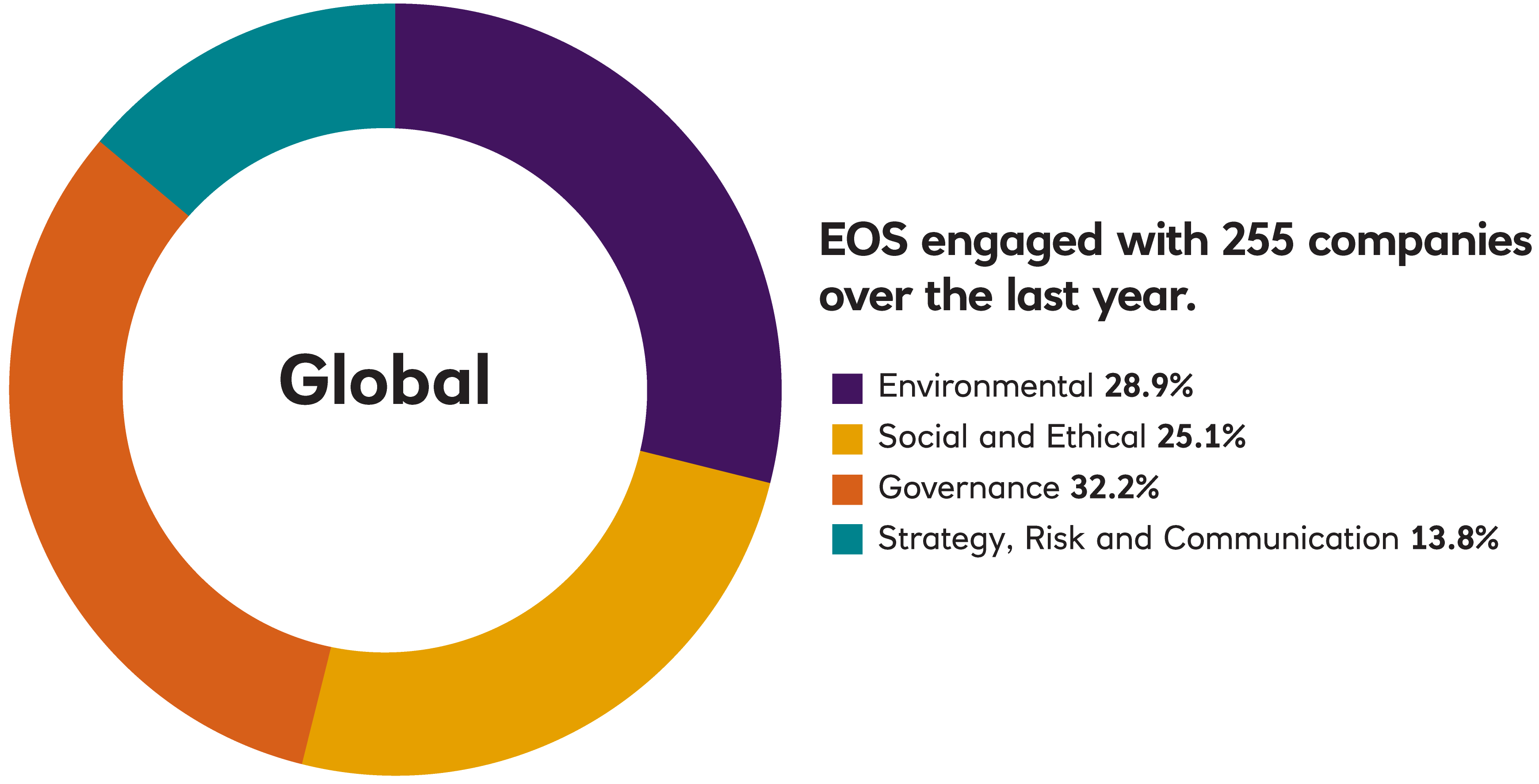
In 2022, EOS engaged with 255 companies on 1,336 environmental, social, governance, strategy, risk and communication issues and objectives. This holistic approach to engagement means that EOS typically engages with companies on more than one topic simultaneously.
In 2021, EOS engaged with 242 companies on 1,132 environmental, social, governance, strategy, risk and communication issues and objectives. This holistic approach to engagement means that EOS typically engages with companies on more than one topic simultaneously.
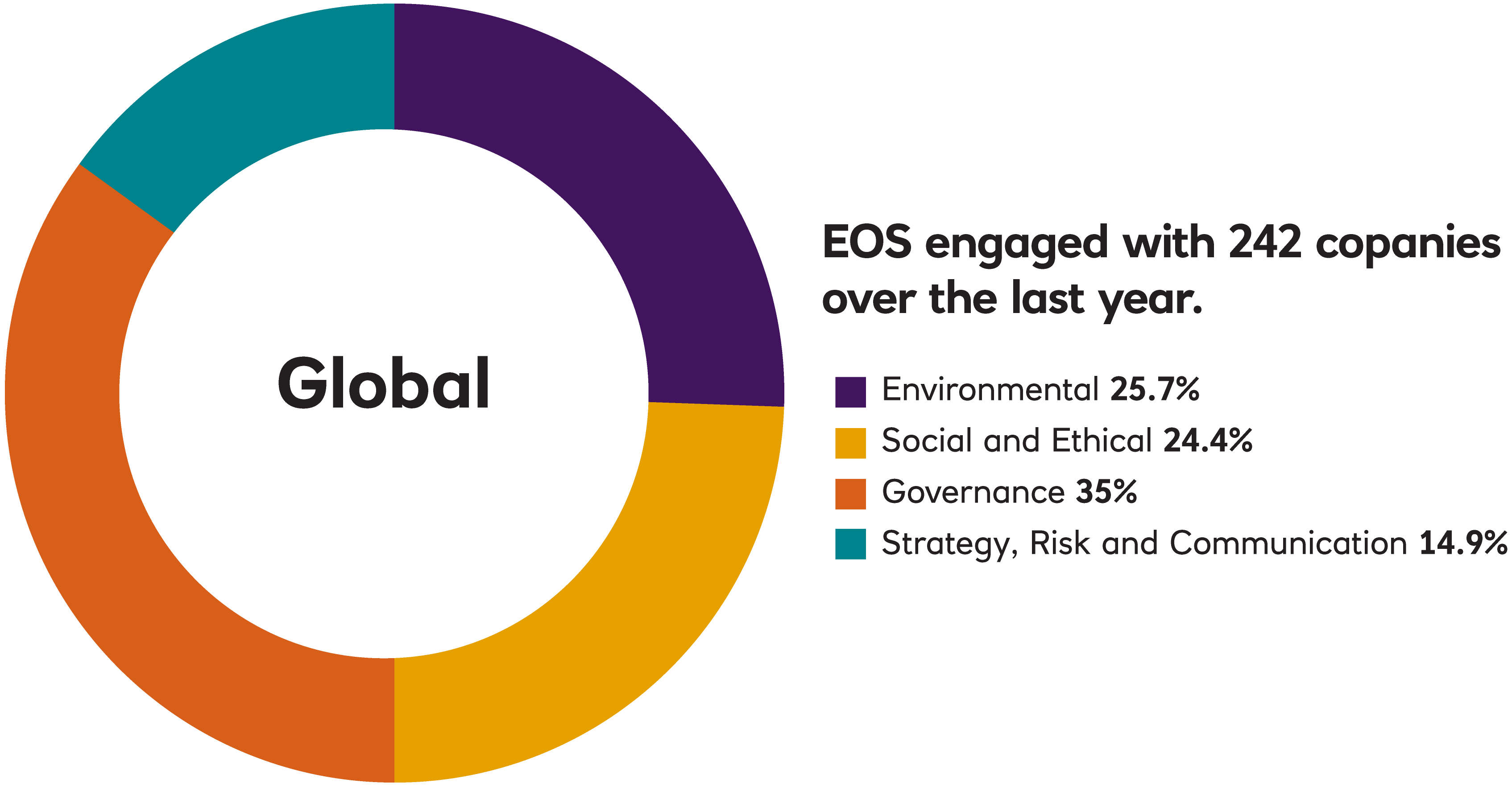
EOS Engagement by Theme
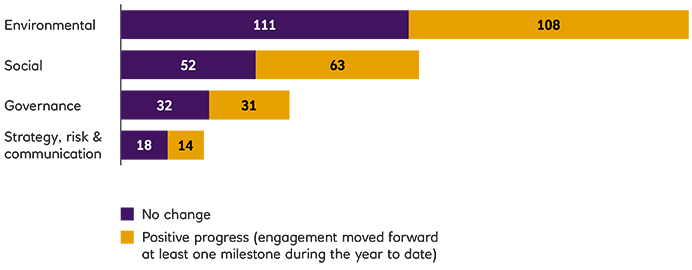
A more detailed analysis of the engagement issues and an analysis of progress on these issues over time, along with further case studies are included in the EOS annual reports. The focus of engagements reflects client priorities that are included in the engagement plan. The engagement process is monitored by EOS based on four milestones beginning with initial awareness and culminating in the implementation of a strategy to address the engagement issue. Milestone progress in the reporting period is shown below:
Case studies
Significant engagement case studies for EOS in the reporting period include the following:
-
Unilever
EOS has been engaging with companies in furtherance of the Finance Sector Deforestation Action (FSDA) initiative. Launched at COP26, the FSDA is a results-driven collaborative of financial institutions that unites signatory organisations around an engagement approach to addressing nature-related risks and opportunities by tackling deforestation, and creating essential convergence across other climate and nature-related initiatives.
EOS met with Unilever’s global sustainable sourcing director together with FSDA participating investors. Unilever said it was making good progress towards its goal to have a deforestation-free and conversion-free supply chain in palm oil, paper and board, tea, soy, and cocoa by 2023. To this end, the company has been reconfiguring and simplifying its supplier base, and determining the connections that smallholders have with independent mills. Unilever has geospatially mapped over 4,000 smallholders in the palm and cocoa supply chains. For soy, it invested in a green refinery in part to solve the untraceable soy issue in Brazil. The refinery will process 500,000 soybeans, a third of which Unilever will use. It has an advanced verification process in place for palm oil and has begun auditing a few big suppliers against its verification framework, leading to more robust numbers.
-
National Grid
Alongside the Climate Action 100+ co-leads, EOS met with the company to discuss the decarbonisation of heat, climate-related policy engagement and the delays in connecting renewable energy capacity to the grid. The company argued that a rapid transition to electrification in its US business would require regulator support and this would create challenges for remaining customer choice. The company is updating its climate policy but does not plan to publish a review of its indirect lobbying via industry associations (due to resource constraints rather than a lack of commitment). The company has identified challenges in connecting new renewable energy sources to the grid. EOS emphasised the importance of setting 1.5°C-aligned targets covering the whole business. The company is engaging with the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) on methodologies for this.
-
BNP Paribas
EOS have asked when the bank would cease all support for new oil and gas projects. In response, BNP have confirmed that it has not directly financed any oil projects since 2016 and that that it would not finance additional capacity. It intends to progressively phase out from companies focused on upstream oil. However, it wants to continue financing key players such as TotalEnergies, which it sees as part of the solution.
-
AIA
AIA’s group head of sustainability reported to EOS that the investment function had rapidly increased its focus on ESG integration and net zero, following extensive internal engagement, before submitting targets to the SBTi. The company seeks to be a leader on climate change over a three-to-five year timeframe. The CEO is committed to this agenda. EOS expressed some concern that the company had not yet disclosed a net-zero roadmap and emphasised the importance of this for maintaining leadership. EOS also reiterated that it would like to see the ambition of its Scope 3 emissions target increased to a 1.5°C scenario. The company said that SBTi was the best practice method for reaching net-zero emissions and argued that its approach was more robust than at other insurers.
-
Siemens
EOS met with Siemens to understand its ambitions around diversity. Whilst there is almost gender balance on the supervisory board, there is only 20% female representation on the executive management board. The company said that with a management board of five it was not pursuing a target for female representation beyond the legal minimum of 20% unless it increased the size of the board. If one of the existing members steps down then the role would be open for appropriately qualified and experienced women to apply. It added that there was more significant female representation at one and two levels below the management board, with good progress towards the respective targets of 30% and 25% by 2025.
-
Pfizer
EOS have engaged with Pfizer on its strategies to manage two systemic risks – climate change and antimicrobial resistance (AMR). The company pointed to its ambitious net zero by 2040 commitment and its role in encouraging its suppliers to commit to a science-aligned GHG reduction target. EOS highlighted the momentum around biodiversity considerations and asked how the company was thinking about its reliance on the natural environment. Pfizer agreed to take this back to the board for further consideration. Pfizer has one of the industry’s largest portfolios of antimicrobials and plays a leadership role in combatting AMR.
-
BMW
Continuing to engage on the theme of forced labour, EOS asked BMW how it ensures that none of its tier one suppliers are involved in the exploitation of Uyghurs in the Xinjiang region. BMW has integrated new tools that track trade and customs data as well as company data, financial interactions, and potential relationships between suppliers. Media screenings, supplier engagement, online assessment with proof of issue resolution, and on-site visits are triggered in critical situations. The process has been checked and legally approved by the German Federal Office of Economics and Export Control recently (BAFA).
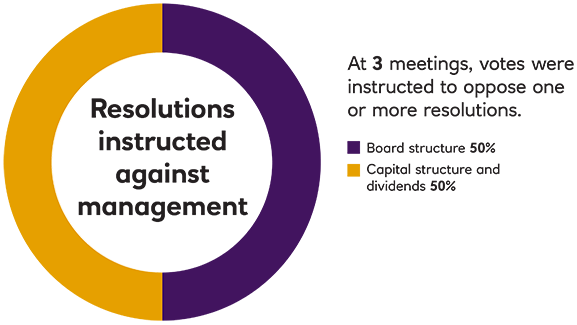
EOS Voting Activity
No significant voting of securities took place in 2023, reflecting the Fund’s transition to a portfolio better aligned to its new strategic objective. The Fund no longer invests in listed equities and voting of credit instruments happens very rarely.
Read more
As a material shareholder in many real assets, the Trustee provides regular input to business and operational decisions including the approval of remuneration, change of auditors, significant supplier negotiations, external financing, capital expenditure and investment approvals. This activity is carried out through RIEL and is focused on managing these assets efficiently in accordance with the approved investment case while applying the ROP. An example includes ongoing involvement in the decision to generate carbon credits from forestry growth at Shasta Cascade Timberlands.